Global Skills Academy

Recovery, Transition, and Transformation, these three pillars serve as the guiding vision of UNESCO’s new Strategy for Technical and Vocational Education and Training (TVET) for the period 2022–2029.
The COVID-19 pandemic severely disrupted both education systems and labor markets, intensifying youth unemployment and the mismatch between skills and job demands. At the same time, it accelerated the pace of the digital revolution. In this context, a fundamental transformation of education systems is urgently needed to respond to a rapidly changing and uncertain future.
In September 2022, the United Nations Secretary-General convened the Transforming Education Summit, where governments around the world pledged to establish more inclusive, resilient, and relevant lifelong learning systems to meet evolving skill demands and facilitate the transition toward green and digital economies.
Driving education transformation requires flexible pathways for skills training, upskilling, and reskilling, and the promotion of lifelong learning. It also demands the identification and anticipation of the skills needed for digital and green economic transitions. Moreover, this transformation depends on strengthening social dialogue and ensuring the engagement of employers and civil society, especially young people.
TVET is deeply interconnected with Sustainable Development Goal 4 (SDG 4), and encompasses multiple dimensions. This strategy repositions TVET as a pathway for individuals to learn, work, and live; as a catalyst for green and digital transformation and sustainable economic development; and as a vehicle for social cohesion and equity. The strategy also acknowledges the impact of climate change, the importance of the informal economy, demographic transitions, and the widespread application of artificial intelligence.
The strategy outlines a transformative agenda to support countries in equipping youth and adults with the skills they need and in providing lifelong learning opportunities for all. It commits to strengthening the relevance of national TVET systems through collaboration with the UNEVOC Network and the Inter-Agency Group on TVET (IAG-TVET), under the lens of lifelong learning.
The strategy also encompasses flagship initiatives such as the Global Skills Academy under the Global Education Coalition. This Academy engages the private sector and international organizations, including the International Labour Organization (ILO) and the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), to deliver digital skills to tens of millions of young people worldwide.
The strategy includes concrete actions such as training TVET teachers and trainers, developing skills monitoring tools to track demand and supply, and updating as well as ensuring cross-border recognition of vocational qualifications.
Today, more than ever, collective efforts are needed to ensure that young people and adults acquire the new skills demanded by emerging jobs, enabling them to unlock their full potential and navigate the profound social, economic, and environmental transformations underway globally. This is also part of a renewed social contract for education—reimagining a more sustainable future for all.

Stefania Giannini
Assistant Director-General for Education, UNESCO
Assistant Director-General for Education, UNESCO

Stefania Giannini
Assistant Director-General for Education, UNESCO
Assistant Director-General for Education, UNESCO

The Global Skills Academy (GSA) is one of the key initiatives under UNESCO’s Global Education Coalition. Launched on 15 July 2020, the sixth annual World Youth Skills Day, the GSA aims to provide one-stop training services to learners through partnerships with over 250 vocational training centers in more than 160 countries and regions, coordinated by UNESCO’s International Centre for Technical and Vocational Education and Training (UNEVOC). Special priority is given to supporting disadvantaged learners.

education, or training (NEET)
The Global Skills Academy serves as a bridge between education and global employment, unlocking the potential of youth and adults to build a better future. Yet, it is estimated that 267 million youth worldwide are still not engaged in employment, education, or training.
The Academy reflects UNESCO’s vision for transforming technical and vocational education and training (TVET) from 2022 to 2029. Through skills development, capacity enhancement, support for productive employment and decent work, the strategy seeks to drive a successful and equitable transformation of TVET. It also aims to guide this transformation toward a more digital, greener, and inclusive economy and society.
UNESCO is committed to supporting its Member States in addressing both current and future TVET challenges. It has outlined three strategic priority areas:
1. Developing the skills needed for learning, work, and life for all individuals;
2. Developing the skills necessary for an inclusive and sustainable economy;
3. Developing the skills required for an inclusive and peaceful society.
UNESCO will work in close collaboration with bilateral and multilateral partners, institutions, governments, the private sector, and educators worldwide, placing TVET at the heart of the global education agenda.




"One More Skill, One More Opportunity"
Embracing the educational philosophy of “One More Skill, One More Opportunity”, the Global Skills Academy, in collaboration with UNESCO-UNEVOC, is advancing the goals of the UNESCO TVET Strategy (2022–2029): Transforming TVET for Successful and Just Transitions. This initiative bridges the worlds of education and employment, helping young people to gain the skills needed for jobs and entrepreneurship—especially in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, which has accelerated the digital transformation of global workplaces.
The Academy focuses on meeting the growing global demand for TVET in STEM fields (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics). It ensures inclusive, equitable, and high-quality education and promotes lifelong learning opportunities for all, contributing to the development of a more inclusive, resilient, and robust global education system.
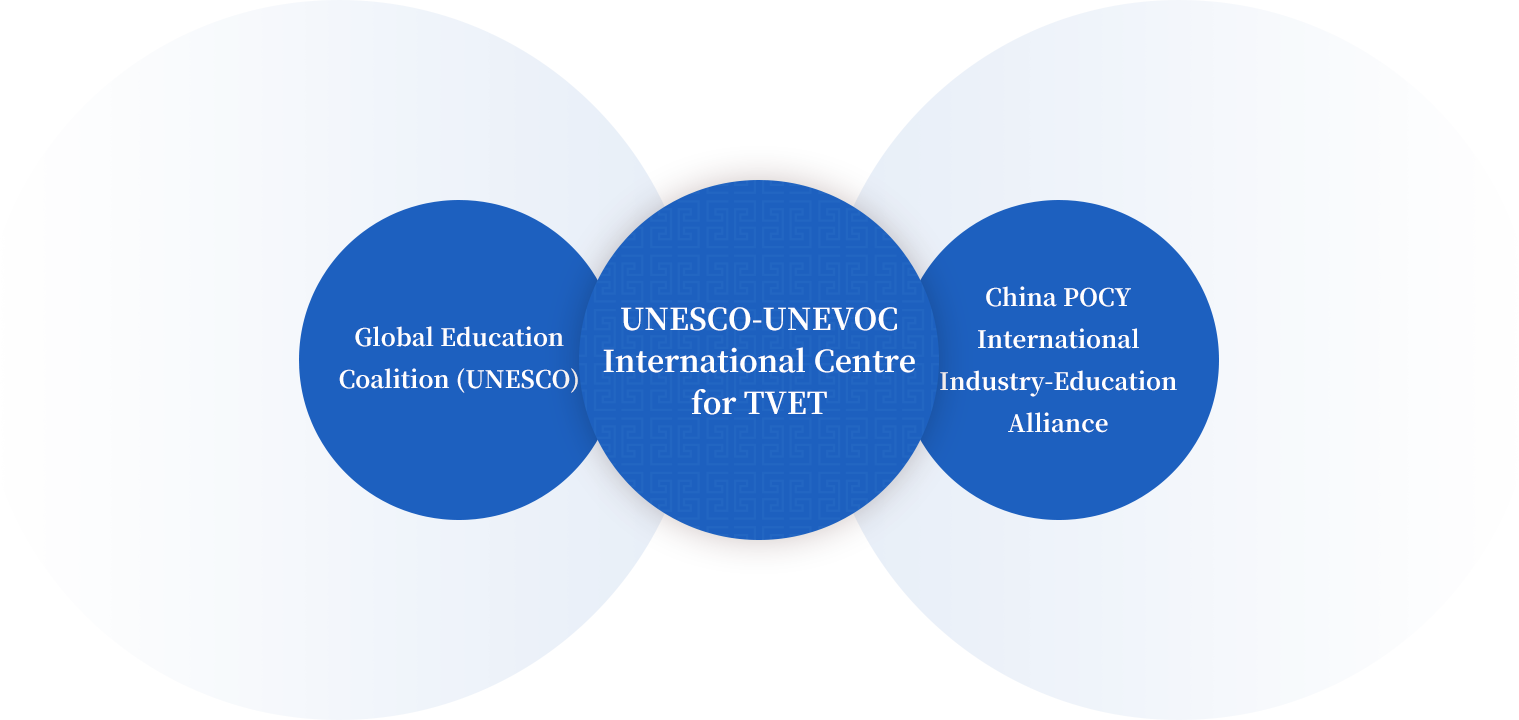
On May 3, 2023, Mustapha Badreddine, President of the World Federation of UNESCO Clubs, Centers and Associations (WFUCA), and Yao Yichun, President of China POCY Group, signed a strategic cooperation agreement at UNESCO Headquarters in Paris. The agreement aims to jointly promote initiatives such as UNESCO Category II Centres, the Global Skills Academy, and the China POCY International Industry-Education Alliance.
In July 2023, marking the third anniversary of the GSA, Global Skills Academy Ltd. (Hong Kong) was officially established under China POCY Group. Guided by the UNESCO Education 2030 Framework for Action, the company actively promotes cooperation under the Global Skills Academy framework across China and the world.

One Core
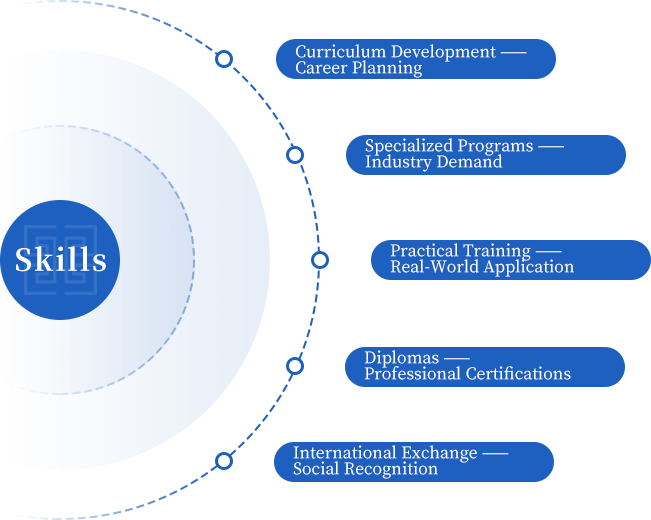
Dual-Engine Model
Degrees + Vocational Training = Employment Upon Graduation
Programs focus on high-demand, specialized fields with strong employment prospects. Students receive highly recognized academic qualifications aligned with national education standards.
Certificate programs are based on national occupational standards and qualification frameworks. They are designed to enhance employability, broaden career options, and improve income and benefits.
Three-Way Partnership Collaboration
Four Dimensions of Empowerment
Global Faculty Network
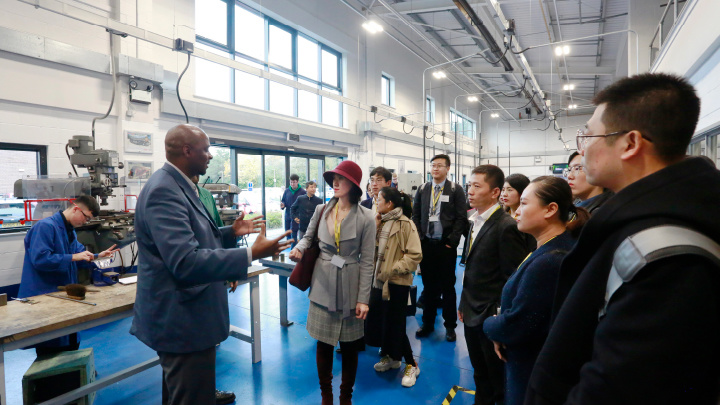
The Global Skills Academy develops a diverse international faculty across languages, disciplines, skills, and applied practice. The teaching staff includes academicians, industry experts, and foreign instructors. Through the UNEVOC Network, regular international lectures further expand students' global competencies.International Study Tours
Embracing the philosophy “The world is the classroom,” the Academy leverages the Global Education Coalition and China POCY’s overseas training bases to offer students at least one international study tour annually. These experiences equip students with cutting-edge industry knowledge and global cultural competence.Skills Competition Training
The Academy adopts a “competition-based training model,” preparing students for global and national skills competitions such as the WorldSkills Competition and China’s National Vocational Skills Competition—enhancing both technical and professional capabilities.Practical Training Integration
Through China POCY’s domestic and international specialized training centers, the Academy implements a “1+1+1” model: 1 year foundational academic learning 1 year hands-on training at industry bases 1 year internships with top global enterprises
Five Core Colleges
Integrated Development Strategy
Driven by collaborative partnerships and talent-focused outcomes, the Academy is building five core institutions aligned with global vocational education trends and world-class standards in key disciplines: Sino-German Institute of Technology; School of Aerospace and Aviation; School of Rail Transit; International Maritime Institute; International School of Nursing.
Sino-German Institute of Technology

School of Rail Transit

International School of Nursing

International Maritime Institute

School of Aerospace and Aviation
Sino-German Institute of Technology
Academic Program Offerings
Intelligent Manufacturing of Composite Materials
Program Code:430603Intelligent Control Technology
Program Code:460303Industrial Robotics
Program Code:460305New Energy Vehicle Technology
Program Code:460702Big Data Technology
Program Code:510205Applications of Artificial Intelligence
Program Code:510209Microelectronics Technology
Program Code:510402
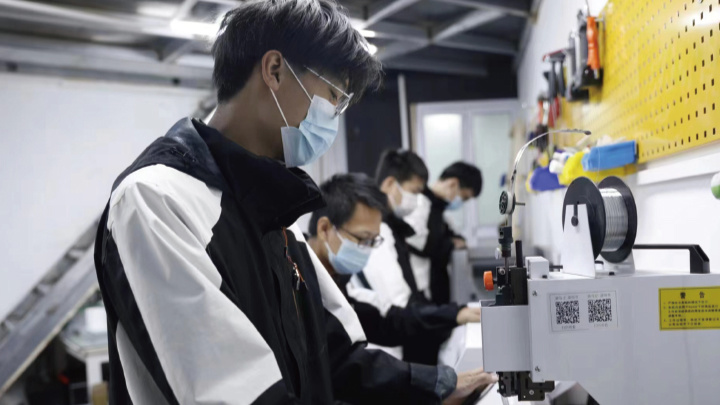
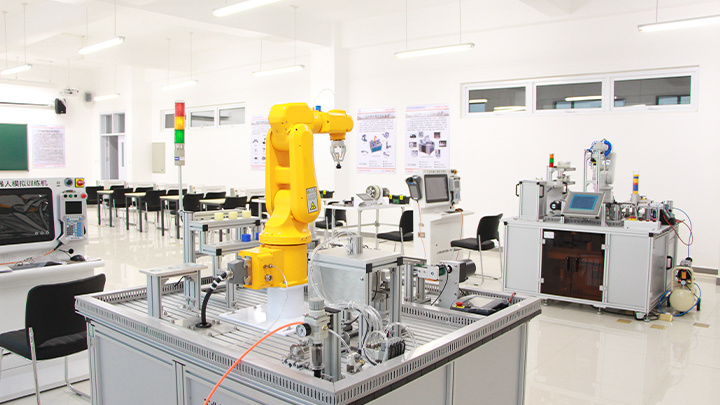




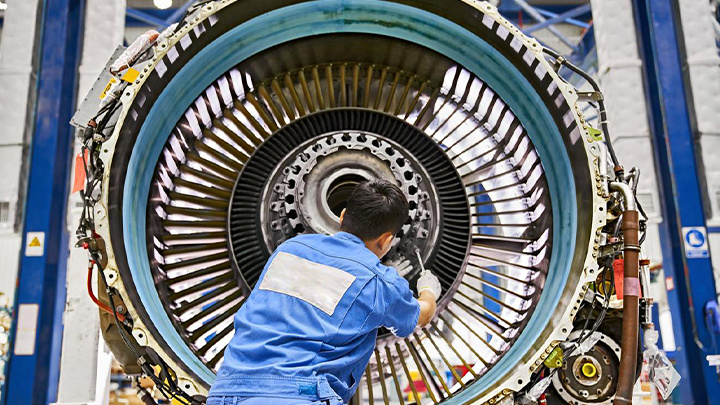
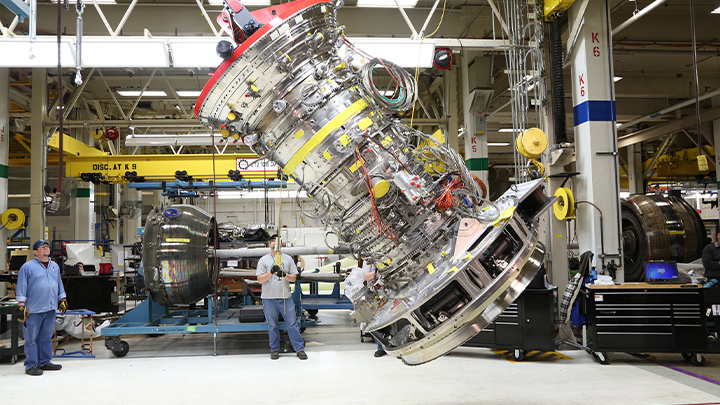
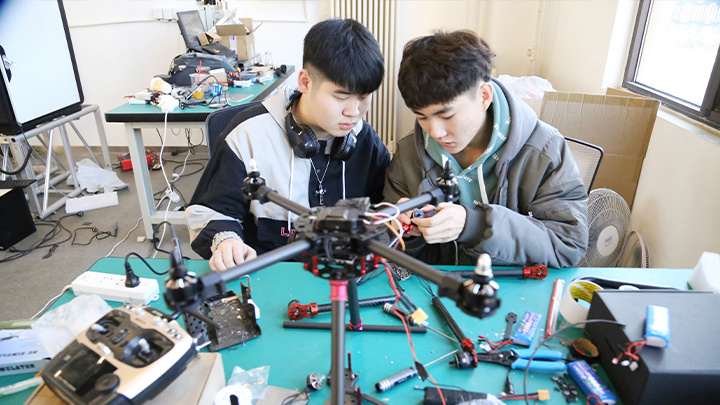
School of Aerospace and Aviation
Academic Program Offerings
Digital Manufacturing of Aircraft
Program Code:460601Aircraft Engine Maintenance
Program Code:460608UAV Applications
Program Code:460609Civil Aviation Transportation
Program Code:500401Aviation Safety and Security Management
Program Code:500406Airport Operations and Management
Program Code:500408
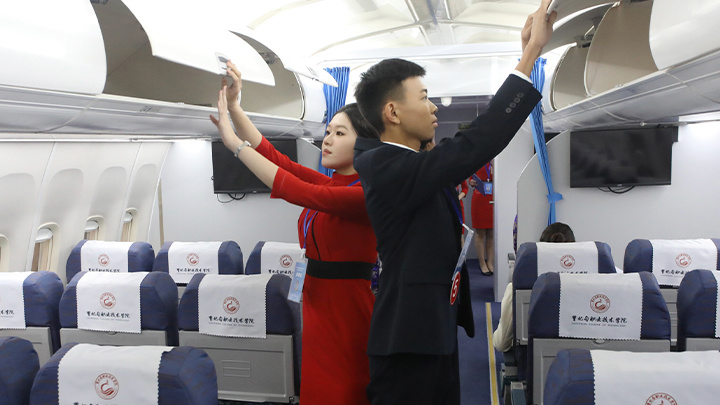




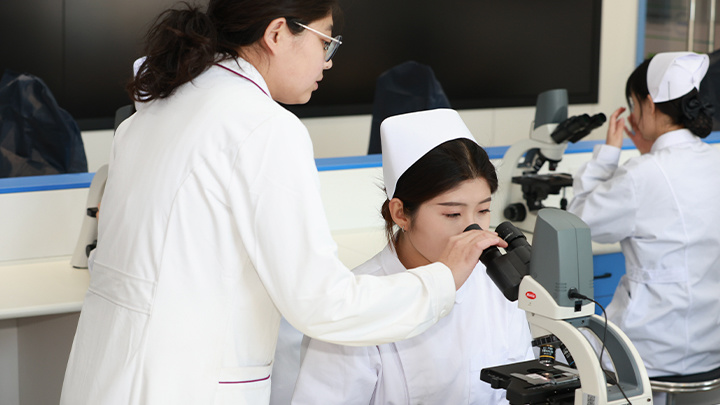
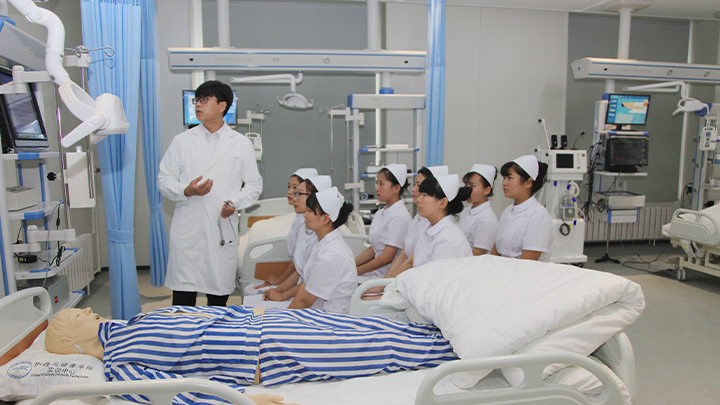
International School of Nursing
Academic Program Offerings
Nursing
Program Code:520201Midwifery
Program Code:520202Medical Aesthetics Technology
Program Code:520507Rehabilitation Therapy Technology
Program Code:520601Health Management
Program Code:520801Smart Elderly Care Services and Management
Program Code:590302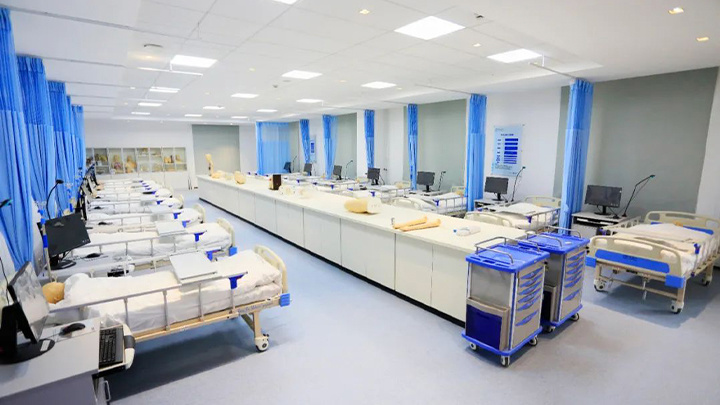



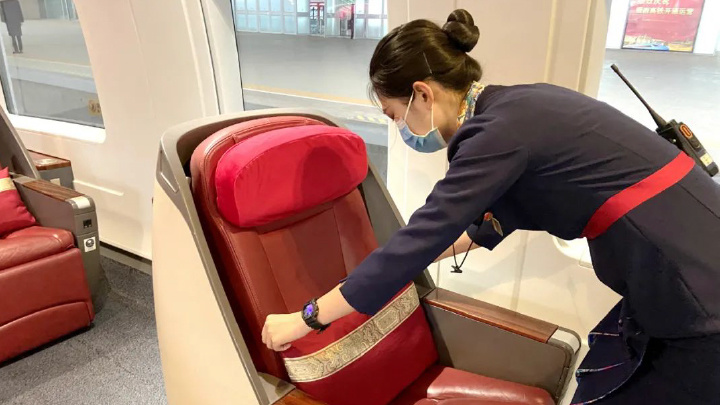
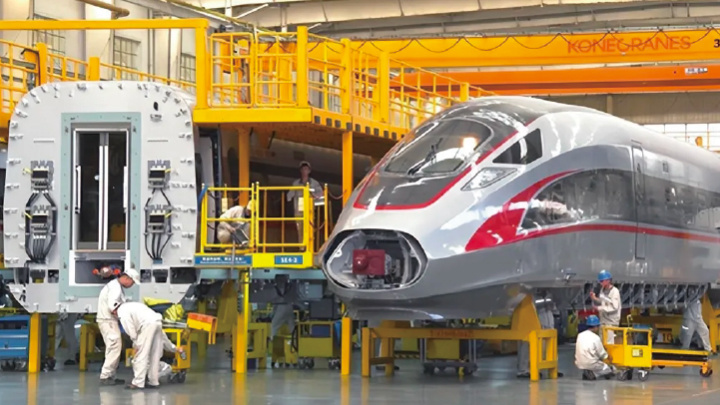
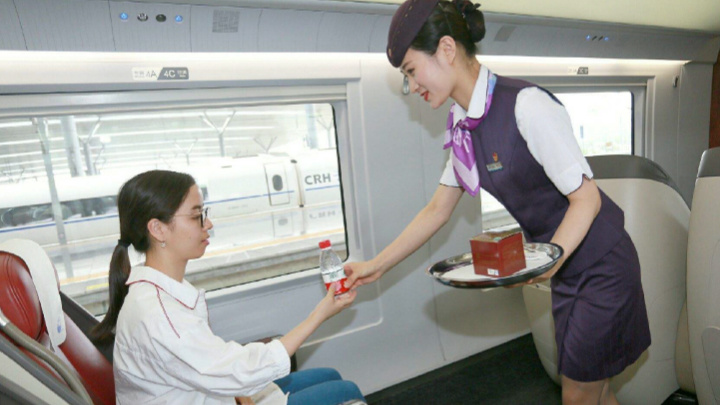
School of Rail Transit
Academic Program Offerings
High-Speed Rail Manufacturing and Maintenance
Program Code: 460402Urban Rail Transit Engineering Technology
Program Code: 500601Urban Rail Transit Vehicle Applications
Program Code: 500602Urban Rail Transit Electromechanical Technology
Program Code: 500603Urban Rail Transit Communication and Signaling
Program Code: 500604Urban Rail Transit Power Supply Technology
Program Code: 500605Urban Rail Transit Operation Management
Program Code: 500606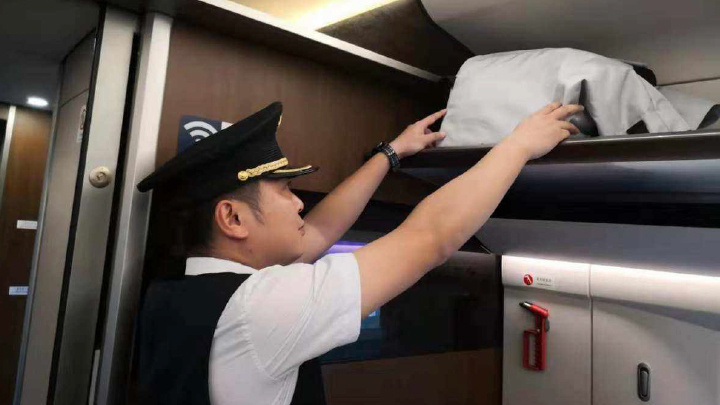




International Maritime Institute
Academic Program Offerings
Aquaculture Technology
Program Code: 410401Navigation Technology
Program Code: 500301Port and Waterway Engineering
Program Code: 500302Marine Engineering Technology
Program Code: 500303International Cruise Service and Management
Program Code: 500304Port Machinery and Intelligent Control
Program Code: 500306Ship Electronic and Electrical Technology
Program Code: 500308















